+91 891 993 2794
info@tajdental.inOral Cancer Symptoms
Introduction:
Oral cancer, a formidable adversary, warrants our attention. Taj Dental recognizes the silent threat affecting the oral cavity – lips, tongue, gums, and throat. Understanding early signs is pivotal for timely intervention, significantly impacting treatment success. Let’s delve into the nuances of oral cancer symptoms, causes, and preventive measures with Taj Dental guiding the way.
Understanding Oral Cancer:
What is Oral Cancer?
Oral cancer is characterized by the uncontrolled growth of malignant cells in the oral cavity. This encompasses various areas, and if left unchecked, these cells can infiltrate surrounding tissues, posing severe health risks. Recognizing its existence is the first step towards effective management.
Types of Oral Cancer
Squamous cell carcinoma stands as the primary adversary in the realm of oral cancer, comprising the majority of cases diagnosed. This aggressive form of cancer originates in the squamous cells, which are flat and thin cells lining the oral cavity. While squamous cell carcinoma is the predominant player, it’s crucial to recognize that the world of oral cancer isn’t a one-size-fits-all scenario.
- Adenocarcinoma: This type of oral cancer develops in the salivary glands, leading to the formation of malignant glandular cells. It necessitates specialized attention due to its distinct biological behavior.
- Mucoepidermoid Carcinoma: A combination of mucous and epidermal (squamous) cells characterizes mucoepidermoid carcinoma. This type is often found in the major and minor salivary glands.
- Verrucous Carcinoma: Known for its slow growth, verrucous carcinoma usually presents as a wart-like growth. While it tends to be less aggressive than squamous cell carcinoma, it requires careful consideration due to its potential impact.
- Spindle Cell Carcinoma: Comprising elongated, spindle-shaped cells, this variant is a less common but noteworthy manifestation. It often poses diagnostic challenges and demands a nuanced approach in treatment planning.
- Minor Salivary Gland Carcinomas: Emerging from the numerous minor salivary glands scattered throughout the oral cavity, these carcinomas exhibit diversity in histological features, making accurate diagnosis and tailored treatment vital.

Causes and Risk Factors:
- Tobacco Use The leading cause of oral cancer is often attributed to tobacco use. Whether through smoking or smokeless products, the carcinogens in tobacco significantly elevate the risk of developing this malignancy.
- Alcohol Consumption Excessive alcohol intake, especially in conjunction with tobacco use, escalates the risk of oral cancer. This synergistic effect underscores the importance of moderation in both habits.
- Human Papillomavirus (HPV) Infection Certain strains of HPV have been linked to oral cancer, emphasizing the need for preventive measures. HPV vaccination is a crucial step in reducing the risk associated with this viral infection.
- Sun Exposure Prolonged exposure to the sun can contribute to lip cancer. Protecting the lips from harmful UV rays with appropriate measures, such as lip balm with SPF, is essential for prevention.
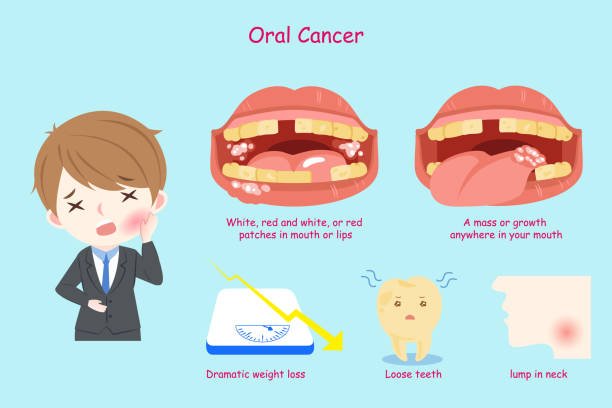
Common Symptoms of Oral Cancer:
1. Persistent Mouth Sores Mouth sores that linger beyond a reasonable healing period should raise concerns. These persistent sores may be indicative of oral cancer and warrant immediate professional attention.
2. Red or White Patches The presence of unusual red or white patches on the tongue or inside the mouth can be an early sign of oral cancer. Regular self-examinations are vital for spotting such abnormalities.
3. Changes in Speech Oral cancer can affect the muscles and tissues involved in speech production, leading to changes in pronunciation or slurring. Any alterations in speech should be investigated promptly.
4. Difficulty Swallowing Dysphagia, or difficulty swallowing, can be a consequence of advanced oral cancer. This symptom underscores the importance of seeking professional evaluation if persistent.
5. Unexplained Weight Loss Unintentional weight loss unrelated to changes in diet or exercise can be a sign of advanced oral cancer. This emphasizes the urgency of addressing symptoms promptly.
The Importance of Early Detection:
Early detection is the linchpin for successful oral cancer treatment. The sooner the malignancy is identified, the more effective the intervention. Regular dental check-ups and heightened awareness of potential symptoms are paramount for early diagnosis.
Oral Cancer Screening:
Regular Dental Check-ups
Dentists play a pivotal role in early detection during routine dental check-ups. These examinations encompass a thorough inspection of the oral cavity, ensuring any anomalies are promptly identified.
Self-Examination
Empowering individuals with the ability to perform self-examinations enhances early detection. Regular self-checks for mouth sores, patches, or other abnormalities contribute to proactive health management.
Seeking Professional Help:
Dentist Consultation
Any persistent oral symptoms should prompt an immediate consultation with a dentist. Dentists can conduct a detailed examination and recommend further diagnostic tests as needed.
Medical Diagnosis and Testing
For a comprehensive diagnosis, medical professionals may employ imaging tests, biopsies, and other examinations. The precise identification of the type and stage of oral cancer is crucial for effective treatment planning.
Treatment Options:
1. Surgery
Surgical removal of the cancerous tissue is often the primary treatment in the early stages of oral cancer. This intervention aims to eliminate the localized malignancy.
2. Radiation Therapy
Utilizing high doses of radiation, this therapy targets and destroys cancer cells. Radiation may be employed as a standalone treatment or in conjunction with surgery or chemotherapy.
3. Chemotherapy
Chemotherapy involves the administration of drugs to either kill or impede the growth of cancer cells. It is a systemic treatment that reaches cancer cells throughout the body.
4. Immunotherapy
Immunotherapy harnesses the body’s immune system to combat cancer cells. This innovative approach enhances the immune response, offering a targeted and effective treatment.
Coping with Oral Cancer Diagnosis:
Coping with an oral cancer diagnosis is a multifaceted journey. Emotional support, whether from friends, family, or support groups, is integral to navigating the challenges that come with the diagnosis. Maintaining a positive mindset is pivotal in the healing process.
Preventive Measures:
Lifestyle Changes
Adopting a healthy lifestyle significantly mitigates the risk of oral cancer. This includes quitting tobacco, moderating alcohol consumption, and maintaining a balanced diet rich in fruits and vegetables.
Vaccination for HPV
HPV vaccination is a proactive measure, especially for individuals at risk. Protecting against specific strains of the virus reduces the likelihood of developing HPV-related oral cancer.
Supporting Oral Cancer Patients:
Supporting individuals diagnosed with oral cancer is paramount. Friends and family play an essential role in providing emotional support during the challenging treatment process. Encouragement, understanding, and empathy contribute to a positive healing environment.
Living Beyond Treatment:
Survivors of oral cancer can lead fulfilling lives post-treatment. Regular follow-ups with healthcare providers, adherence to a healthy lifestyle, and ongoing support from loved ones contribute to a positive outcome.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, vigilance regarding oral cancer symptoms, coupled with proactive measures, is pivotal for early detection and successful treatment outcomes. Regular dental check-ups, self-examinations, and lifestyle modifications are crucial components of a comprehensive strategy against oral cancer.
Frequently Asked Questions:
1. How common is oral cancer?
Oral cancer constitutes a small percentage of overall cancer cases, but its impact is significant. Regular screenings can aid in early detection.
2. Can oral cancer be prevented entirely?
While not entirely preventable, adopting a healthy lifestyle and getting vaccinated against HPV substantially reduce the risk of oral cancer.
3. What is the survival rate for oral cancer?
Survival rates vary based on the stage of diagnosis. Early detection markedly improves the chances of successful treatment.
4. Are there long-term side effects of oral cancer treatment?
Treatment may have side effects, but with proper care and support, many individuals lead fulfilling lives post-treatment.
5. How often should one undergo oral cancer screening?
Regular dental check-ups are recommended, with individuals at higher risk potentially requiring more frequent screenings.

Leave A Comment